You’ve finally decided to upgrade or buy a new Ultra HD TV. The picture quality of your old TV just doesn’t cut it anymore.
The new 2024 OLED, QLED, 4K UHD, and 8K models produce more than four times the resolution of your old HDTV.
You’ve narrowed down the screen size you want and decided whether to go with a flat or curved TV screen. This is where most people get confused.
Often, many people will search for OLED vs 4K. They are comparing two completely different things.
Did you know there are OLED TVs that are also 4K? Also, 4K televisions are not OLED.
To clear everything up, let’s quickly examine OLED and 4K.
 LG 65-Inch Class OLED evo C2 Series Alexa built-in 4K Smart TV, 120Hz Refresh Rate, AI-Powered 4K, Dolby Vision IQ and Dolby Atmos, WiSA Ready, Cloud Gaming (OLED65C2PUA, 2022)
LG 65-Inch Class OLED evo C2 Series Alexa built-in 4K Smart TV, 120Hz Refresh Rate, AI-Powered 4K, Dolby Vision IQ and Dolby Atmos, WiSA Ready, Cloud Gaming (OLED65C2PUA, 2022)
OLED vs 4K

The real question is: What is another 4K TV display technology that compares with OLED 4K TV displays?
For most budgets, you’ve got one other choice: 4K LED (UHD or Ultra HD) LCD panel technology.
Most TVs sold today are based on LCD screen technology. We often refer to them as LED LCD TVs or just LED TVs because these sets use an LED backlight.
OLED is a newer, competing TV technology that is gaining in popularity.
So, what is the difference between 4K UHD and OLED TVs?
This article will explain the differences between these two TV types and discuss why you might choose one or the other.
We will help you make sense of each television technology and then show you the difference.
We will also show you which offers more satisfying home entertainment viewing experiences based on your budget.
 Sony 65 Inch 4K Ultra HD TV X80K Series: LED Smart Google TV with Dolby Vision HDR KD65X80K- 2022 Model
Sony 65 Inch 4K Ultra HD TV X80K Series: LED Smart Google TV with Dolby Vision HDR KD65X80K- 2022 Model
What is a 4K LED?

LED stands for light-emitting diode and is the oldest and least expensive HDTV technology.
LED-based LCD TVs use “light-emitting diodes” behind the liquid crystals. LEDs are little solid-state devices that make light due to the movement of electrons through a semiconductor.
They’re ranged in clusters behind the panel (called ‘back-lit’ LCD LED TVs) or on the sides (called ‘edge’ or ‘edge-lit’ LED TVs).
Back-lit or edge-lit LED TVs significantly improve contrast levels over fluorescent-based LCD TVs. These panels show deeper blacks for more depth of an image.
LCD LED TVs display brighter, richer, and more vibrant colors. Thinner and lighter than older television technology, making table and wall mounting much more effortless
LED TVs are less expensive than OLED technology. They provide the most outstanding selection in size and brand.
They’re a great value, and you can buy an LED TV in virtually any size you want.
There are a few drawbacks. Since LED TVs get their light from an external source, the size of the HDTV increases.
LED televisions can’t produce a true black. In blackout scenes, you’ll notice uneven brightness and a lack of shadow detail in dark areas of the screen.
Adding 4K to LED TVs
4K (UHD or Ultra High Definition) refers to the number of horizontal display pixels on the screen (4096 by 2160 pixels). The new 4K Ultra HDTVs have four times the resolution of the 1080p display. You’re in the range of 8 million pixels for any size screen.
Adding 4K technology, the level of picture quality is startlingly better than on the televisions you’ve watched in the past. There is less fear of pixelation as you approach the TV since the pixels are a lot smaller and grouped tighter.
No matter how close you get or how big the screen is, you’re unable to see the individual pixels on the screen. That’s why the picture quality on a 4K TV is simply stunning.
LED Pros and Cons
- More Affordable
- Available in any TV size
- Lightweight for mounting
- Bright and colorful
- Beautiful picture quality
- Average contrast
- Narrower viewing angle
- Aging technology
- Uneven darkness in blackout scenes
What is OLED?

Pronounced ‘oh-led’, OLED stands for “organic light-emitting diode”. Newer OLED TVs are made from carbon-based materials.
When electricity is applied through them, they emit light that glows either red, green, or blue.
Most OLED televisions are only a couple of millimeters thick. OLED TVs are incredibly thin because each pixel has its own light source.
These televisions are thinner than LED TVs because no back-lighting is required.
You can control images at the pixel level in an OLED display. Each pixel self-illuminates, so OLED TVs deliver unprecedented contrast ratios and exceptional brightness compared to older LED back-lit TVs.
OLED TVs are much more energy-efficient than other TV panel types. In an OLED panel, organic films are placed between semiconductors and supplied with an electrical current.
Every pixel can be switched on and off individually. This makes total black possible and uses less power to create peak brightness levels. This unlimited contrast means OLED panels deliver the whitest whites and the darkest blacks.
These televisions respond lightning-fast and deliver beautiful colors.
Is OLED a 4K TV? The latest LG OLED TVs offer 4K resolution. Watching an OLED TV for the first time is a pure ‘Wow’ moment.
The downsides? OLED TVs are very expensive, and no one is quite sure how long OLED panels will last.
OLED TVs are only available in large sizes: 55 inches and bigger. LG is the only company that currently manufactures OLED panels for TVs.
Sony has an agreement with LG to put LG OLED panels into certain Sony televisions. Otherwise, you won’t find OLED in other televisions sold in the U.S.A.
OLED Pros and Cons
- The slimmest TV
- Wider viewing angle
- Highest contrast
- More accurate blacks
- Brighter colors
- Faster refresh rate
- Limited screen sizes
- Muted brightness
- More expensive
- Unknown lifespan
What is the difference between OLED and LED?
The lighting source is the significant difference. Each pixel of the OLED’s carbon-based “organic light-emitting diode” is its own light source. In contrast, all the pixels in an LCD TV are illuminated by “light-emitting diodes” (LED) back or edge lights.

13-Point OLED vs. 4K LED TV Comparison
Now let’s compare the two technologies head-to-head. Since OLED is a premium TV technology, we have compared it to premium LED TVs.
Let’s see how they stack up, one-on-one when it comes to essential features such as black levels, brightness, contrast, viewing angle, and other key performance considerations.

Each OLED pixel contains red, green, and blue elements, which work together to create millions of excellent color combinations.
LED TV tech has improved significantly over the last few years. However, since the Liquid Crystal Display requires LED backlights, they still lack the depth and richness of OLED TV colors.
Since each OLED pixel contains all the elements needed to produce every color in the spectrum, true colors are more accurately reproduced by OLED technology than LEDs.
Our tests reveal OLED TVs produce richer, deeper, greater color accuracy and color volume than 4K LED TVs.
Winner: OLED TV
LED backlighting can produce brilliant whites and almost unlimited levels of brightness. There is no backlight, and the size of each organic light emitting diode pixel (OLED) somewhat limits brightness.
Winner: 4K LED TV
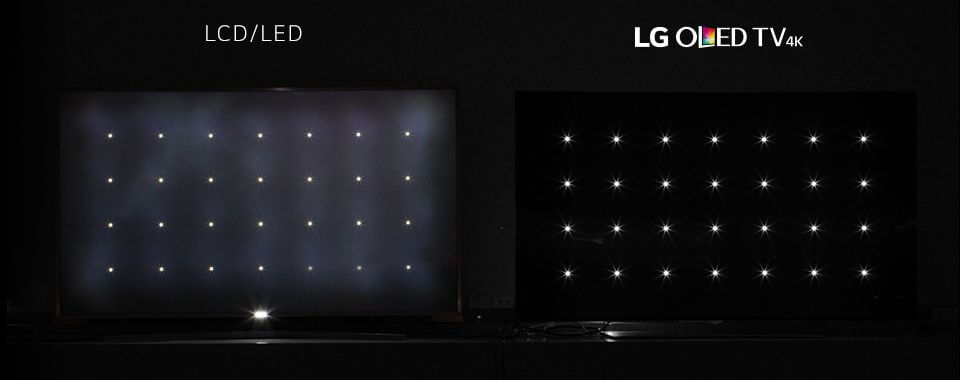
A TV screen’s ability to display deeper black levels is arguably the most important element in producing an excellent picture image.
Dark blacks create higher contrast and richer colors. These specific features allow for a more realistic and brilliant image.
The individually lit OLED pixel offers unlimited grayscale and deeper blacks. Deep blacks are near perfect in the new OLED TVs.
While there have been incredible improvements in LED TV black levels, they will never match OLED TVs in this area.
LED backlights shine behind an LCD panel in LED LCD TVs. 4K LED TVs rely on advanced dimming technology, which selectively dims LEDs that don’t need to be on at full blast.
As a result, LED TVs can suffer from an effect called “light bleed”, where lighter sections of the screen create a glow in adjacent darker areas.
This is not a problem for OLED TVs. An OLED pixel doesn’t produce any light when it does not get electricity. Therefore, it produces the deepest blacks because it is totally black.
Winner: OLED TV

Incredible clarity and sharpness is a major strength of new 4K TVs. The millions of screen display pixels produce great depth and detail.
OLED TVs can create ‘motion artifacts.’ Motion artifacts create a slight blurriness around the edges of images.
Winner: 4K LED TV
Screen uniformity applies to how consistent the image is distributed across the screen. A uniform screen displays an image quality that remains consistent in terms of brightness, color, and clarity at all points along the display area.
Screen uniformity is a drawback specifically related to LED TVs. It is due to having backlights rather than individually lit pixels.
Turning the backlight setting down usually alleviates the problem.
By contrast, since each pixel cell is lit individually, OLED TVs have an extremely even spread of light across the picture. Screen uniformity really enhances the beauty of the entire image.
Winner: OLED TV

. Image Source
As a result of even lighting from each individually lit pixel, OLED TVs display excellent side angle viewing.
While 4K LED TVs are getting better, increasing the viewing angle, they still lag behind OLED models.
It is due to the LED backlights being farther away from the front of the screen panel.
Winner: OLED TV
LG Signature OLED Wallpaper TV
Response time is the time it takes for each individual diode to change from “on” to “off”. A faster response time creates less motion blur.
OLED currently produces the fastest response time of any TV technology today.
The individual OLED pixels are lightning-fast. The LED TV diodes are much slower and operate in a cluster of pixels, not individually. These factors result in a slower change between “on” and “off” states.
Winner: OLED TV
OLEDs have made significant strides in this area. However, the size range is still limited compared to LED TVs.
Screen sizes for OLED models usually begin at 55 inches. Even though OLED displays are now pushing 90+ inches, they are still dwarfed by the largest 4K LED screen sizes.
100+ inch LED displays are now being offered to the public.
Winner: 4K LED TV
Over time, LED bulbs will fade, and screen uniformity will degrade. Economically replacing LED backlights is not currently possible.
OLED technology is new and untested. True longevity is unknown.
LG says its OLED TVs can be watched 5 hours a day for 54 years before they fall to 50 percent brightness. That claim remains to be seen, as OLED TVs have only been out since 2013.
We give the OLED vs LED lifespan nod to 4K LED panels because of this uncertainty.
Winner: 4K LED TV
They require less power overall.
Winner: OLED TV
Samsung UHD: Experience the world in 4K
When you consider the most important picture quality elements, specifically deeper blacks create better contrast, resulting in brighter colors and picture depth. OLED screens get my vote for overall picture quality.
Winner: OLED TV
Winner: 4K LED TV
When you consider the significant savings you can enjoy, it’s hard to pass up a top-quality 4K LED TV.
Winner: Draw
OLED vs 4K: Side-by-Side Comparison
| FEATURE COMPARISON | OLED TV | 4K LED |
| True Color: | ✔️ | |
| Brightness: | ✔️ | |
| Black Levels: | ✔️ | |
| Sharpness & Clarity: | ✔️ | |
| Screen Uniformity: | ✔️ | |
| Viewing Angle: | ✔️ | |
| Response Time: | ✔️ | |
| TV Size: | ✔️ | |
| Lifespan: | ✔️ | |
| Power Consumption: | ✔️ | |
| Overall Picture Quality: | ✔️ | |
| Price: | ✔️ | |
| Overall Value: | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| OVERALL SCORE: | 7.5 | 5.5 |

Should I buy an OLED or 4K LED TV?
The decision to purchase an OLED vs 4K LED TV can be challenging. What you decide to buy essentially comes down to the budget.
Is OLED worth it? If money is no object, no question about it, go for an OLED.
If the price is more of a consideration, choose a mid-range or premium full-array back-lit 4K LED TV.
They might not have quite the same contrast level and pure black levels, but they can come very close. Your wallet will thank you.








