60Hz/120Hz/240Hz/480Hz
These are related to the screen refresh rates of HDTV televisions. Early LCD TVs were 60Hz. That is they redraw the screen 60 times per second. Improved or faster refresh rates combat motion blur and judder. The higher the number, the faster the rate or the number of times the picture is redrawn per second.
1080i
1080i means that the resolution of the picture is 1920 vertical pixels by 1080 horizontal pixels and “i” stands for interlaced scanning. Interlaced scanning is based on the principle that the screen shows every odd line at one scan of the screen and then all the even lines in a second scan.
1080p
1080p means that the resolution of the picture is 1,920 vertical pixels by 1,080 horizontal pixels and p stands again for progressive scanning. This format works on the same principle as 720p; the only difference is that in this type there are more pixels and the resolution is better.

16:9
16:9 is the aspect ratio of a movie screen and widescreen DTV formats used in all HDTV (High Definition TV) and some SDTV (Standard Definition TV); it stands for 16 arbitrary units of width for every 9 arbitrary units of height.
24p
24 frame per second progressive-scan video. Since the film is recorded at 24 frames per second TVs that have this feature will not have judder when displaying the film source.
3-2 Pulldown Processing
Sophisticated video processing is common in progressive-scan DVD players and TVs. It corrects for distortion and artifacts that occur when film-based material (at 24 frames per second) is converted to video (30 frames per second), then de-interlaced to create a progressive-scan signal.
3D TV
Whether a 3D TV uses OLED or LCD screen technology, the basic idea at work in all 3D TVs is creating “left” and “right” versions of the image on the screen. Like 3D movies, 3D TV requires that each viewer wear special glasses to see the 3D effects. The job of 3D glasses is to get the correct version of the image to the correct eye. Whether your TV uses active shutter glasses or polarizing passive glasses, your brain combines the images it receives from your right and left eyes into a seamless whole. Most 3D TVs require the use of battery-powered “active shutter” glasses, though some TVs work with lightweight passive glasses that are virtually identical to the glasses handed out in movie theaters. Many believe that 3D TVs create a more engaging viewing experience, by adding a sense of picture depth.
4:3
4:3 is the aspect ratio of traditional squarish National Television Systems Committee (NTSC) TV screens; it stands for four arbitrary units of width for every three arbitrary units of height.
4K
A high-resolution digital display and video formats with a horizontal resolution of around 4000 pixels. 4K UHD is a resolution of 3840 pixels x 2160 lines (8.3 megapixels, aspect ratio 16:9). 4K has twice the horizontal and vertical resolution of the 1080p HDTV format, with four times as many pixels overall.
720p
720p means that the resolution of the picture is 1,280 vertical pixels by 720 horizontal pixels and p stands for progressive scanning. Progressive scanning offers a smoother picture as 720 horizontal lines are scanned progressively or in succession in a vertical frame that is repeated 30 times a second.
Active Shutter Glasses
For most 3D TVs, to see three-dimensional effects, each viewer must wear a special type of 3D glasses called “shutter” glasses. Active glasses are far more technologically advanced than the disposable passive 3D glasses handed out in movie theaters. These battery-powered liquid-crystal glasses are able to lighten or darken hundreds of times per second to alternately block out the left or right lens in coordination with the video frames flashing on the screen. The lenses aren’t displaying images, just switching between dark and clear. To anyone not wearing shutter glasses, a 3D TV picture will look blurry.
Advanced Television Systems Committee (ATSC)
Advanced Television Systems Committee is responsible for establishing and developing digital television standards, as well as all 18 formats of Digital TV.
Anamorphic Video
When widescreen video images have been “squeezed” to fit a narrower video frame when stored on DVD, we call it anamorphic video. These images must be expanded (un-squeezed) by the display device. Today’s TV screens employ a 16:9 aspect ratio, so that widescreen and anamorphic videos can be viewed in their proper proportions. Images appear unnaturally tall and narrow when an anamorphic video is displayed on old-fashioned TV sets with a 4:3 screen ratio.
Anti-blur Technology
A technology that reduces image “motion blur” that can sometimes occur with LED LCD TVs. LED LCD TVs with anti-blur technology can deliver smoother, clearer images during fast-paced scenes.
Artifacts
Artifacts are defined as unwanted visible effects in the picture caused by disturbances and errors in video transmission or digital processing. Artifacts include ‘edge crawl’ or ‘dot crawl’ or ‘hanging dots’ in analog pictures, and ‘pixelation’, ‘contouring’ or ‘blockiness’ in digital pictures.
Aspect ratio
Aspect ratio is the ratio of width to height of a TV screen. It may be either the traditional squarish 4:3 ratio of the National Television Systems Committee (NTSC) TV screen or the 16:9 ratio of widescreen DTV formats for all HDTV (High Definition) and some SDTV (Standard Definition).
ATSC
Named for the Advanced Television System Committee. ATSC is the digital replacement for NTSC.
Audio Return Channel
A TV with Audio Return Channel allows a single HDMI cable to carry the audio from the TV’s built-in tuner “upstream” to a compatible A/V receiver, eliminating the need for a separate optical or coaxial digital audio cable. This feature is found on most 2010-and-newer TVs and audio/video components with HDMI 1.4 connections.
Audio/Video Inputs
Audio/Video or “AV” inputs connect a DVD player, cable box, streaming device, video game controller, or another video component to your TV. Most modern HDTVs now use HDMI cables for these inputs.
Bezel
The frame of the TV that surrounds the screen.
Bandwidth
Bandwidth, in general, means the amount of information that can be carried in a given time period (usually a second). More exactly, it is a range of frequencies used for transmitting picture and sound information from the transmitter to your TV. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has allocated 6 MHz for TV broadcasters for each channel.
Bit Rate
Bit rate is measured as “bits per second” (bps) and refers to the rate at which the data is transmitted. For Digital TV, the maximum possible bit rate within the bandwidth is 19.4 Mbps while SDTV has a lower bit rate. The higher the bit rate, the more data is processed which usually results in higher picture resolution or better sound quality.
Child Lockout/V-Chip
Allows parents restrictive authority over what their children watch. Child Lockout: restricts access to certain channels with a special code. V-Chip: select the maturity level of appropriate programming based on the TV Rating System.
CFL Backlight
LCD TV backlighting is provided by a Cold Cathode Fluorescent Light. This is the backlight found in most LCD televisions
Codec
Codec is a short-term for ‘Coder-decoder’. This device is used to convert analog video and audio signals into digital format, and vice versa, it can also convert received digital signals into an analog format.

Component Video
Analog video inputs that split the video signal between up to three cables. Video information is either sent in RGB or YPbPr signals. Component video can carry progressive scans and high-definition signals.
Composite Video
An analog video input where the video signal is carried on a single cable. It cannot carry high definition or progressive scan signals.
Contrast Ratio
The ratio of the luminance of the brightest white to the darkest black that a TV can display at any one time.
Compression
Compression allows the delivery of more programs in a single channel. It is an electronic manipulation of digital data that reduces and removes redundant and/or non-critical information in the digital picture and sound without noticeably degrading picture quality. One of the compression methods is called MPEG-2.
CRT (Cathode-Ray Tube)
CRT stands for a cathode-ray tube. Invented in 1897, even nowadays it is the most common display technology for televisions. The tube uses an electron beam to scan lines on the screen coated with phosphor, which glows when struck by the beam. The other display technology being used more and more often nowadays in television sets is LCD.
Device Control
HDMI connections between devices not only carry video and audio they also can carry control signals. Manufacturers call these different things such as Viera Link or Bravia Link and it allows a single remote to control various devices of the same brand. It can also do things like automatically turning on a Blu-Ray player when that input is selected.
DLNA
Digital Living Network Alliance, is a standard that allows communication and content sharing between DLNA-compatible devices. Unlike manufacturer-specific features, DLNA is a standard and will work across brands.
Dolby Digital (Dolby AC-3)
Dolby Digital, also called Digital 5.1 or AC-3, is a five-channel surround sound system that delivers CD-quality digital audio and provides five channels of full frequency for front left, front right, center, surround left, and surround right speakers, plus one channel for LFE (low-frequency effect) subwoofer. It is the official audio standard for Digital TV and HDTV.
DTV (Digital Television)
DTV stands for Digital Television. It refers to all-digital television formats and standards established by the Advanced Television Systems Committee (ATSC). Two basic DTV standards are HDTV (high-definition television) and SDTV (standard-definition television)
Dynamic Contrast Ratio
This is the best contrast a display can do over time, in reality, it is a marketing device to allow manufacturers to advertise extreme contrast ratios by manipulating conditions to give the best possible result. A calibrated display’s contrast ratio will never approach the Dynamic Contrast Ratio.
EDTV (Enhanced-Definition Television)
EDTV stands for Enhanced Definition Television. The picture quality of EDTV is superior to that of standard analog TV (480i) but not as good as HDTV (1080i or 720p). EDTV displays the picture at a resolution of 852×480 (480p) lines in either 4:3 or 16:9 aspect ratios and it includes the Dolby Digital sound system.
EPG
EPG stands for the electronic program guide. It is a system displaying channels and program data on-screen.
Flat-panel TV
Flat-panel TV typically displays pictures using gas plasma or LCD technology and is only a few inches thick.
Front-projection TV
Front-projection TV comprises 2 parts: a separate front projector (usually placed on a table or ceiling-mounted) and a reflective screen (or simply a wall). The projector is placed at one end of the room, the screen is at the other end, and the speakers may be placed wherever they will provide you good sound experience. The picture can be rather large but remember; the larger the picture, the more visible the pixels or scan lines and the darker the image.
Ghosting
Ghosting means multiple overlaid TV images or ‘ghosts’ which you can notice around the objects while watching TV. Ghosting is caused by the broadcast signal traveling to your TV through various obstacles, for example, hills or tall buildings, and your antenna picks up the original TV signal along with signals reflected by the obstacles. If the ghosting is changing rather than static, it may be caused by the signal reflected by flexible objects, for example, trees.
HDMI
High Definition Multimedia Interface. A digital input format that can carry uncompressed video and up to 8 audio channels. It can also send and receive signals for compatible device control and it has built-in content protection.
HDTV (High-Definition Television)
HDTV stands for High Definition Television. This highest-resolution subset of Digital Television offers filmlike picture quality with impressive surround sound. With twice the vertical and horizontal picture resolution, the picture of HDTV is approximately twice as sharp as that of NTSC. HDTV has a widescreen aspect ratio of 16:9 and a Dolby Digital sound system. Currently used HDTV formats – 1080i and 720p both offer reduced motion artifacts like ghosting and dot crawl.
Interlaced Scanning
Interlaced scanning is a method based on the principle that the screen shows every odd line at one scan of the screen and then all the even lines in a second scan. There are 30 frames shown per second and this can make the larger screen flicker, which is the usual problem with interlacing. However, LCD and plasma screens cannot display interlaced signals and must first convert them to a progressive format, and then they can display the transmitted images.
Internet Connectivity
– Many HDTVs are now equipped with a built-in RJ45 (ethernet) input or WiFi (built-in or optional) to enable them to connect directly to the internet. They don’t provide the same access as a computer with a web browser but they offer features like Yahoo! widgets for instant access to news, sports scores, weather, stock quotes, and more. Many can connect to YouTube or other video clip services, picture sharing services like Flickr, and social networking sites like Twitter or Facebook. Video-on-demand services such as NetFlix, HULU, or Amazon on-demand are also available.
Judder
Also called telecine judder, this is an unwanted effect from converting film, which is 24 frames per second, to a video which is 29.97 frames per second. It is most noticeable as a skipping effect during slow camera pans.
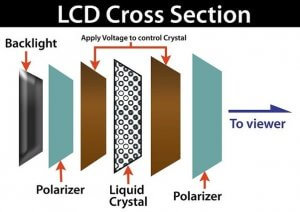
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)
LCD stands for Liquid Crystal Displays. It refers to a flat panel technology that uses liquid crystals sandwiched between two glass plates for example in laptop computers, other small portable displays, and also in televisions. Wide-screen HDTVs are available with displays of adequate resolution up to about 37 inches.
LED Edge Lighting
In the form of LCD television backlighting where LED lights are placed around the edge of the panel, the color and contrast are generally superior to fluorescent light and also allow for extremely thin construction.
Light Sensors
Many newer HDTVs are equipped with light-sensing devices that let the TV automatically adjust the picture and back-lighting based on the lighting in the room. This feature can save energy but not a very significant amount.
Letterbox
Letterboxing means copying the widescreen format with an aspect ratio of 16:9 to video format with an aspect ratio of 4:3. The result of this process is that the full picture is presented only on the middle part of the screen, with black bars above and below it. This arrangement is referred to as ‘Letterbox’ and you can see it on your 4:3 TV while watching movies. On a 16:9 TV, letterboxing does not block out so much of your screen and makes your experience more profound.
Local Dimming LED
A form of LCD television backlight that uses banks of controllable LED lights behind the panel. The light banks can be dimmed and brightened to give far superior contrast to fluorescent backlighting. Most use white LEDs but red, green, and blue LEDs have also been used for more color control. This is considered the best currently available backlighting for LCD TVs.
Motion Blur
Motion blur is a phenomenon specific to LCD panels, it occurs when the response time and refresh rate of the TV cannot keep up with motion on the screen which can trail to appear behind fast-moving objects.
NTSC (National Television Systems Committee)
NTSC or National Television Systems Committee is the organization that develops technical standards for black-and-white television and color television. The term is also used to refer to the video-transmission standard used in the western hemisphere, Japan, and other Asian countries. NTSC established the 525-line (480 visible) analog broadcast TV standard. It is supposed to be soon replaced by digital broadcast standards.
OLED
Pronounced ‘oh-led’, OLED stands for ‘organic light-emitting diode’. When electricity is applied through them they emit light that glows either red, green, or blue. Newer OLED TVs are made from carbon-based materials.
Over-the-air Broadcast (OTA)
Over-the-air Broadcast is also called Terrestrial Broadcast. It is standard over-the-air broadcast to an antenna, as opposed to satellite or cable transmission.
PAL
Phase Alternating Line is the broadcast television standard used in much of Europe, Africa, South Asia, and Australia.
Passive 3D Glasses
Passive 3D glasses are like those given out in theaters for watching 3D movies. Although most 3D TVs require active shutter glasses, a few HDTVs work with passive 3D glasses. Passive glasses don’t flicker, like active 3D glasses. Unlike active glasses, passive glasses don’t require a battery.
Picture-in-picture (PIP)
Picture-in-picture is a television feature in which you can see one program inside a small window on the screen while watching another program on the large background screen. You can choose whatever you wish. You can watch two TV programs simultaneously or you can watch TV and video or DVD at the same time.
Pixel
Pixel comes from the words ‘picture element’ and it refers to the smallest element in a television picture. Pixels are single displayable video dots from which the overall picture is made up.
Plasma Displays (PDP)
A plasma display is created by thousands of tiny tubes filled with ionized gas in a plasma state. Ionized gas is very light and flat-panel TVs made by this technique can be even hung on the wall! Plasma displays offer excellent resolution and color and they are the most suitable for the home theatre.
Progressive Scanning
Progressive scanning is used by some HDTVs. Progressive scanning offers a rather smooth picture as 720 or 1080 horizontal lines are scanned progressively or in succession in a vertical frame that is repeated 30 times a second. Some displays, for example, LCD and plasma use progressive scanning methods, while CRTs may use progressive (e.g. in computer monitors) or interlaced scanning methods.
QAM
Quadrature amplitude modulation is the standard that digital cable systems use to transmit video.
Rear Projection
Rear projection is a TV system where the picture is projected against a mirror inside the cabinet and you can watch it as you would an average television. Until recently, the rear projection TVs comprised three CRTs but the new types of rear projection TVs include LCD.
Refresh Rate
The number of times the screen is redrawn per second is represented as Hertz.
Resolution
The resolution reflects the density of lines and dots per line which make up a visual image. It is measured by the number of pixels displayed. The level of resolution directly affects picture quality. Usually, a higher number of lines and dots means also a sharper and more detailed picture. Analog TV has a little over 200,000 color pixels while HDTV, with 1080 vertical pixels and 1920 horizontal ones, has more than 2 million pixels creating the image.
Response Time
This specification represents the amount of time it takes for one pixel to go from active (black) to inactive (white) and back to black again. Applies only to LCD panels.
RS232
A serial port is often used to connect professional calibration or control hardware to the television.
S-Video
An analog video input that splits the video into two signals, uses a 4-pin DIN connector on a single cable. It cannot carry high definition or progressive scan video but offers a better standard definition signal than composite video.
SDTV (Standard-Definition Television)
SDTV stands for Standard Definition Television. The SDTV picture, having either 4:3 or 16:9 aspect ratios, is better and of higher quality than the NTSC, however, it does not reach the quality and resolution of HDTV. SDTV is based on 480 lines of vertical resolution and in both interlaced and progressively scanned formats.
SECAM
Is an abbreviation for Sequential Color and Memory, the broadcast standard used in France, Russia, Central Asia, and some of Africa.
Set-top Box (STB)
The set-top box is responsible for receiving, converting, and sending the picture and sound of the broadcast to the associated television. If your HDTV-ready TV has no built-in HDTV tuner you must connect it to a compatible HDTV STB first. Until then it will not receive and display digital television programs.
THX
THX is a quality assurance standard. For television to be THX certified it must meet certain standards of predictable reproduction of film source content.
UHD
Ultra High Definition television is also known as Ultra HD, UHD, and UHDTV. Ultra-high-definition includes 4K UHD (2160p) and 8K UHD (4320p) and is capable of carrying and presenting native video at a minimum resolution of 3840 x 2160 pixels.
Widescreen
Widescreen TV is a television with a 16:9 aspect ratio. 16:9 is the aspect ratio of the movie screen and widescreen DTV formats used in all HDTV (High Definition TV) and some SDTV (Standard Definition TV); it stands for 16 arbitrary units of width for every 9 arbitrary units of height.